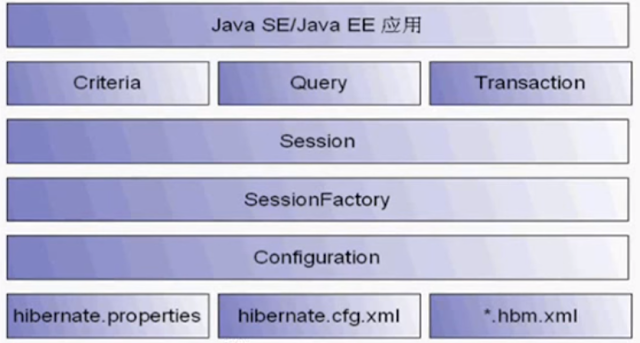
Hibernate API
ORM(Object Relation Mapping)
pojo: plain ordinary java object
A pojo object
- Has at least a primary key field
- other fields
- public get/set functions
- a non-parameter construct function(for hibernate reflection use)
Configuration :
Load hibernate.cfg.xml
Manage ORM files
Load driver, url, login
Manage hibernate configs
SessionFactory :
Get session instance from SessionFactory
Initialized when application starts
Occupied large memory, only need one instance for each database, so use singleton for each database
Cache sql statements and some data (session level cache)
Session : generated from sessionFactory
http://gvace.blogspot.com/2015/12/hibernate-session.html
Transaction : transaction is required, so remember to commit
Example
Employee pojo -> employee table
hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">root</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://192.168.56.101:3306/hibernate</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="com/gvace/domain/Employee.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Employee.hmb.xml
hmb.xml file: manage relationship between a pojo class and a table
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!-- Generated Feb 26, 2016 10:59:22 PM by Hibernate Tools 3.4.0.CR1 -->
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.gvace.domain.Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" type="java.lang.Integer">
<column name="ID" />
<generator class="increment" />
</id>
<property name="name" type="java.lang.String">
<column name="NAME" not-null="true"/>
</property>
<property name="email" type="java.lang.String">
<column name="EMAIL" not-null="true" />
</property>
<property name="hiredate" type="java.util.Date" >
<column name="HIREDATE" not-null="true"/>
</property>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
Employee.java
pojo class, require serialize
package com.gvace.domain;
public class Employee implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3742562662542696434L;
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String email;
private java.util.Date hiredate;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public java.util.Date getHiredate() {
return hiredate;
}
public void setHiredate(java.util.Date hiredate) {
this.hiredate = hiredate;
}
public Employee() {
}
}
Example of using the pojo
@Test
public void test(){
//1. Initiate config, load config file
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");
//2. Create SessionFactory, normally use singleton
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry;
serviceRegistry = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties()).build();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
//3. Create session
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
//4. Start a transaction
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//5. Add an employee
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setName("abc");
employee.setEmail("abc@abc.com");
employee.setHiredate(new Date());
//6. Save
session.save(employee);
//7. Commit
transaction.commit();
//8. Close session
session.close();
}
No comments:
Post a Comment